Substitution At Allylic And Vinylic Carbons

Joong youn shim phillip f.
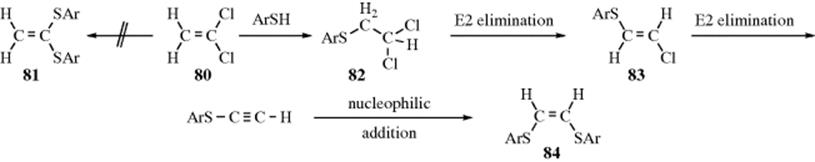
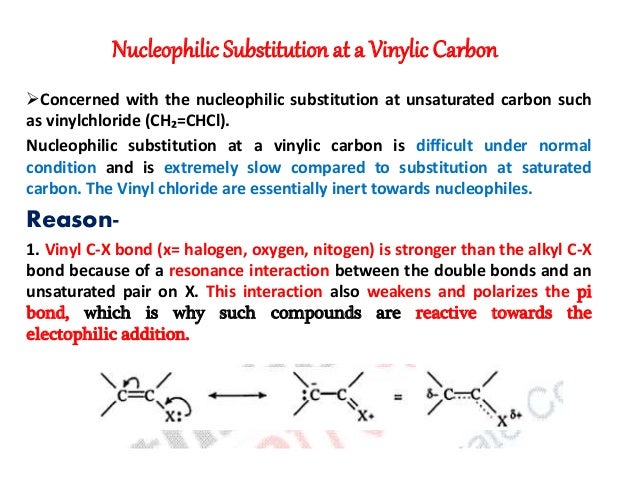
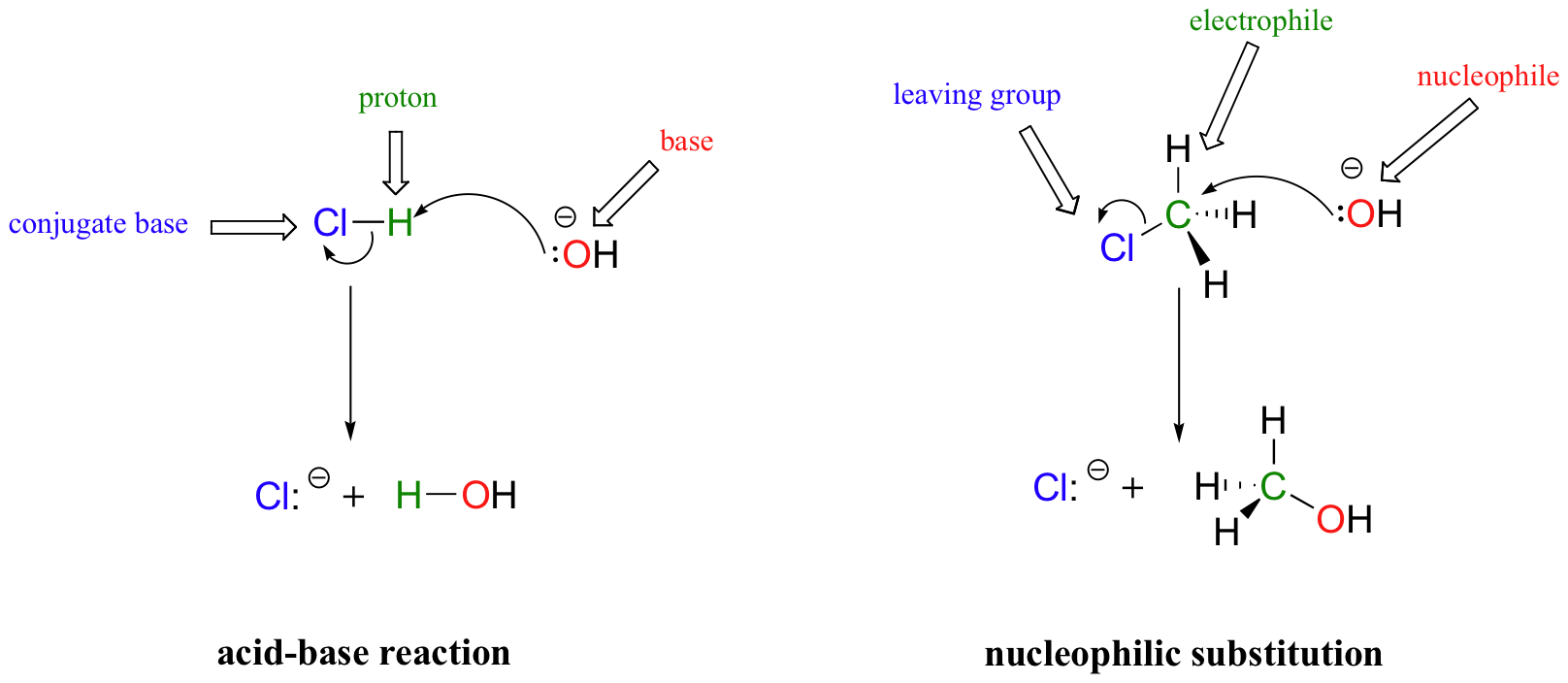
Substitution at allylic and vinylic carbons. It is encountered in nucleophilic substitution. Since both carbon atoms form a double covalent bond so both are sp 2 hybridized. An allylic rearrangement or allylic shift is an organic reaction in which the double bond in an allyl chemical compound shifts to the next carbon atom. The double bonded carbon atoms can be classified as vinylic and allylic carbon atoms.
It provides plenty of examples including allylic and vinyli. The key difference between allylic and vinylic carbon is that allylic carbon is the carbon. In reaction conditions that favor a s n 1 reaction mechanism the intermediate is a carbocation for which several resonance structures are possible. Journal of the american chemical society 2001 123 24 5787 5793.
The general formula for vinyl group is r ch ch 2 in which both carbon atoms are bonded with double bond and r is attached at vinylic position. The allylic carbon atom is more reactive than normal. Key difference allylic vs vinylic carbons functional groups are very important in understanding the different physical and chemical properties of organic molecules the terms allylic and vinyl carbons indicate whether the carbon atom is bonded directly or indirectly to a double bond in a molecule. Allyl indicates a functional group with structural formula h 2 c ch ch 2 r where r is the rest of the molecule it consists of methylene bridge ch 2 in between the vinyl group ch ch 2 and the rest of the molecule therefore allyl group contains sp 2 hybridized vinyl carbon atoms and sp 3 hybridized allyl carbon atom.
Inversion versus retention of configuration for nucleophilic substitution at vinylic carbon. Boone and ann m. As the table below shows the dissociation energy for the allylic c h bond is lower than the dissociation energies for the c h bonds at the vinylic and alkylic positions. See also allylic hydrogen.
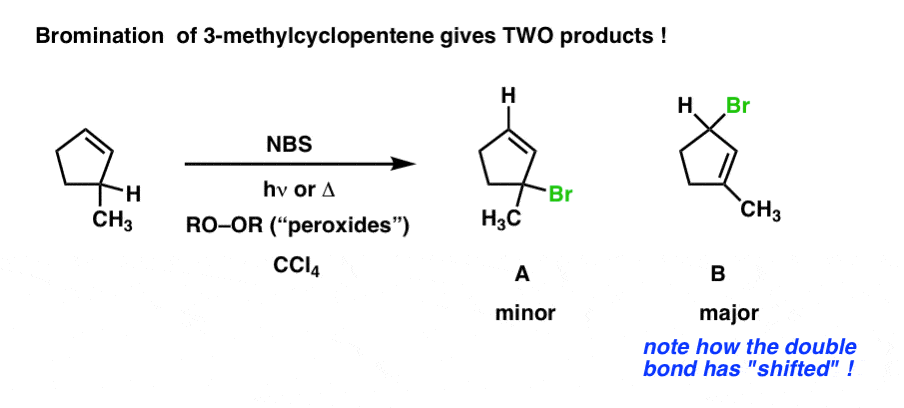
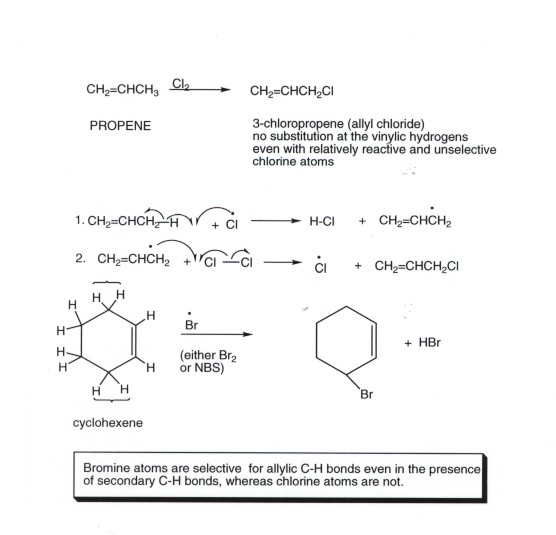
An allylic carbon is a carbon atom bonded to a carbon atom that in turn is doubly bonded to another carbon atom. This organic chemistry video tutorial explains how to determine which carbocation is most stable. The product is an allylic halide halogen on carbon next to double bond carbons which is acquired through a radical chain mechanism.